Global warming, a consequence of human activities altering the Earth’s climate, is a pressing environmental concern with far-reaching implications. This exploration looks into the mechanisms of global warming, its causes, effects, and the urgent need for mitigation strategies to safeguard the planet’s future.
Introduction to Global Warming:
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to a warming effect known as the greenhouse effect.
Key greenhouse gases contributing to global warming include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases. Human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, significantly increase the concentrations of these gases.
The Greenhouse Effect:
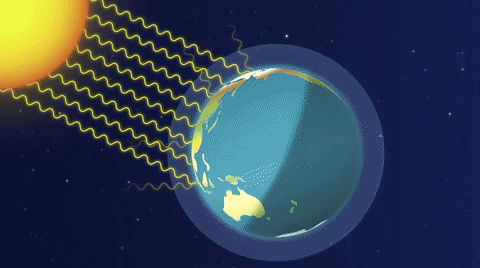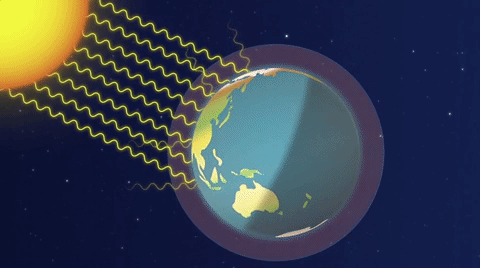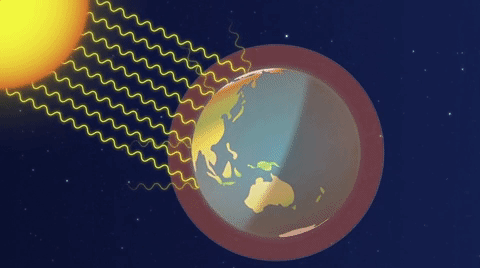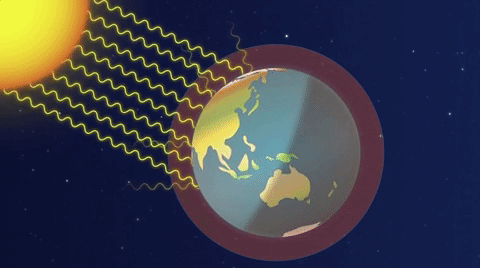
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon crucial for maintaining Earth’s temperature within a range conducive to life. Solar radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, and some of this energy is re-emitted as infrared radiation.
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect: Human activities intensify the greenhouse effect by releasing additional greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap more infrared radiation, leading to a warming of the Earth’s surface and a disruption of the delicate balance in the climate system.
Causes of Global Warming:
The combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, for energy production is a major contributor to global warming. This releases large quantities of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect.
Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture and other purposes reduces the number of trees that can absorb and store carbon dioxide. This results in increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, contributing to global warming.
Industrial Processes: Certain industrial activities release potent greenhouse gases, including methane and fluorinated gases. Agriculture, waste management, and manufacturing processes contribute to the release of these gases into the atmosphere.
Effects of Global Warming:
Temperature Rise: The primary and most evident effect of global warming is a rise in average global temperatures. This warming trend is observed in surface temperature records, as well as the increasing temperatures of oceans.
Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels: Global warming accelerates the melting of glaciers and ice caps, contributing to rising sea levels. This poses threats to coastal communities, ecosystems, and low-lying islands, increasing the risk of flooding and erosion.
Changes in Weather Patterns: Global warming alters weather patterns, leading to more frequent and severe weather events. This includes heatwaves, droughts, intense storms, and shifts in precipitation patterns, impacting agriculture, water resources, and ecosystems.
Ocean Acidification: The absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the world’s oceans leads to ocean acidification. This phenomenon poses a significant threat to marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells, such as corals and certain shellfish.
Mitigation Strategies:
Transition to Renewable Energy: A crucial step in mitigating global warming is transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy offer sustainable alternatives that reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees and restoring forests are effective strategies for sequestering carbon dioxide. Trees absorb CO2 during photosynthesis and store carbon in their biomass, helping to offset emissions from human activities.
Energy Efficiency Measures: Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices in industries, transportation, and buildings reduces overall energy consumption, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Adopting sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision farming, agroforestry, and organic farming, can reduce emissions from the agriculture sector and enhance carbon sequestration in soils.
International Agreements:
Paris Agreement: The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, is a landmark international accord aimed at limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Countries committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing climate resilience.
Kyoto Protocol: The Kyoto Protocol, established in 1997, was an earlier international agreement that set binding targets for developed countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. It laid the groundwork for subsequent climate agreements.
Role of Individuals:
Sustainable Lifestyle Choices: Individuals can contribute to mitigating global warming through sustainable lifestyle choices. This includes reducing energy consumption, using public transportation, recycling, and supporting eco-friendly products.
Advocacy and Education: Raising awareness about the causes and consequences of global warming is essential. Advocacy for policy changes, participating in environmental initiatives, and educating communities about sustainable practices contribute to collective efforts.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
Economic and Political Challenges: Transitioning to a low-carbon economy faces economic and political challenges. Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability requires innovative policies, incentives, and global collaboration.
Urgency of Action: The urgency of addressing global warming is underscored by the potential for irreversible damage to ecosystems and societies. Timely and concerted efforts are needed to limit temperature rise, adapt to changes, and protect vulnerable communities.
Global warming, driven by human activities, presents a complex and urgent challenge that requires concerted global efforts. Understanding its causes, effects, and mitigation strategies is essential for fostering sustainable practices and ensuring a resilient future for the planet. By embracing renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, international cooperation, and individual responsibility, humanity can strive to mitigate the impacts of global warming and build a more sustainable and climate-resilient world.