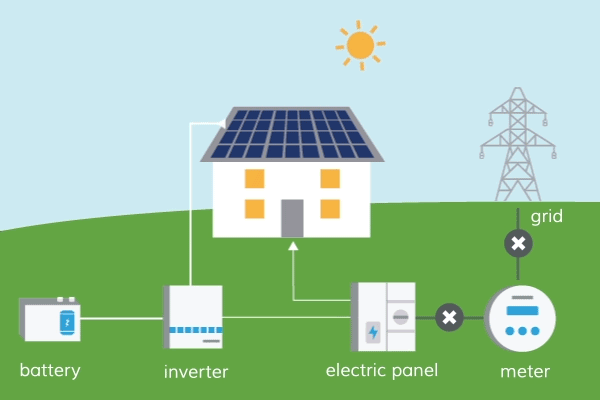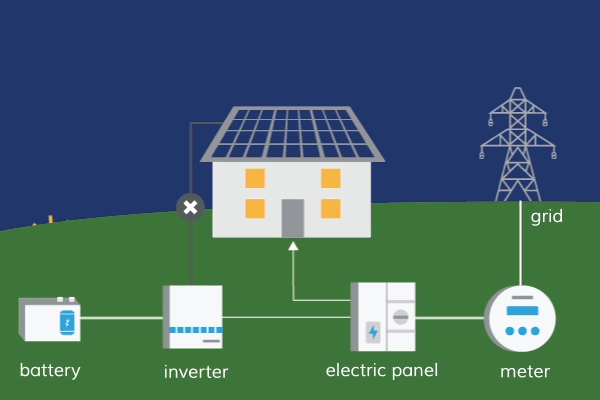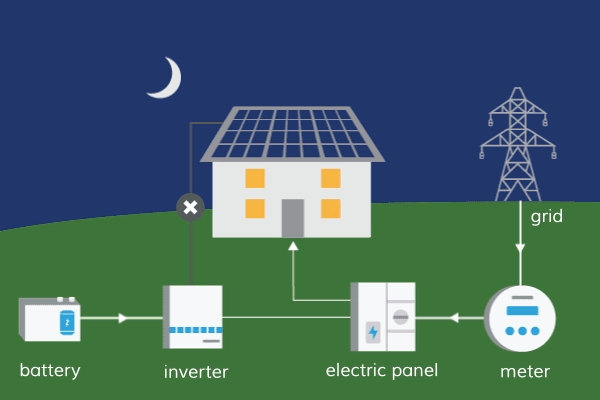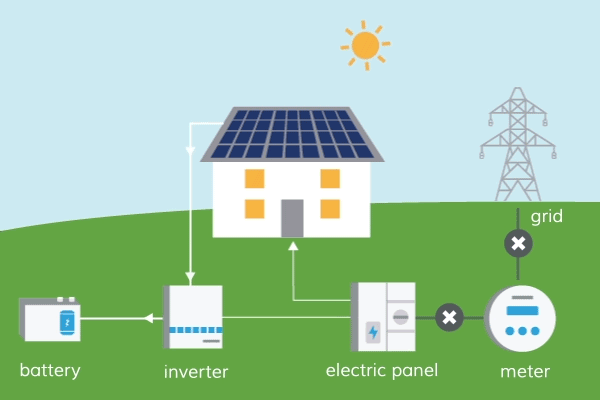
Energy is one of the most essential resources for our day-to-day activities, and we can’t function without it. Among other things, our homes, businesses, and vehicles all require energy in order to function properly.
Renewable and nonrenewable sources of energy are the two primary classifications that can be applied to the field of energy. These two different types of energy each have distinct qualities as well as repercussions for the economy, society, and the natural world. We are going to go into more depth about renewable and non-renewable sources of energy in this blog post.
Renewable Energy
Wind, solar, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass are all examples of sources of renewable energy. These types of energy come from natural resources that can be replenished over time. In comparison to non-renewable energy sources, renewable energy sources offer a number of benefits.
To begin, they are abundant and widely available, which makes them an excellent alternative to fossil fuels, which have a limited supply and are getting even more difficult to find. Second, renewable energy sources are clean and do not release potentially harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere; as a result, they are an option that is friendly to the environment.
One of the most common types of renewable energy is wind energy, which is produced by converting the power of the wind into usable energy. Wind turbines are devices that harness the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electricity. This electricity can then be used to power buildings such as homes and businesses. Solar power is another type of renewable energy that sees widespread adoption.
Solar panels are able to convert the energy that is received from the sun into usable electricity. Another type of renewable energy is hydroelectric power, which is generated by harnessing the kinetic energy of moving water. In many parts of the world, residential and commercial buildings receive their power from geothermal sources, which are powered by the heat produced by the Earth’s interior. Another type of renewable energy is biomass energy, which derives its power from the breakdown of organic substances like wood and the byproducts of agriculture.
Energy That Is Not Renewable
Non-renewable energy, also called fossil fuels, comes from things like coal, oil, and natural gas that can’t be made again over time. This type of energy is also referred to by its other name, non-renewable energy. The use of non-renewable energy sources comes with a number of drawbacks.
To begin, there is a limited supply of them, which is only going to decrease over time. Second, they are responsible for the emission of harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which is a contributing factor to the change in the climate. Third, they are costly to extract and transport and their prices are highly susceptible to shifts in the international market.
One of the non-renewable energy sources that is utilized on the greatest scale is coal. In addition to its use in the production of steel, it is also put to use in the generation of electricity. Oil and natural gas are two additional significant forms of non-renewable energy that are primarily put to use as fuels in the heating and transportation industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, renewable energy sources and non-renewable energy sources each have their own unique characteristics as well as effects on the economy, society, and the environment. Renewable energy sources are an excellent alternative to fossil fuels due to their superior characteristics of being abundant, widely available, pollution-free, and sustainable.
On the other hand, the use of non-renewable energy sources results in the release of harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, their availability is limited, and their extraction and transportation are both costly endeavors. It is essential that we continue our research into renewable energy sources and invest in them as we work toward a future that is more sustainable. This will help us become less reliant on energy sources that do not replenish themselves and will mitigate the effects of climate change.