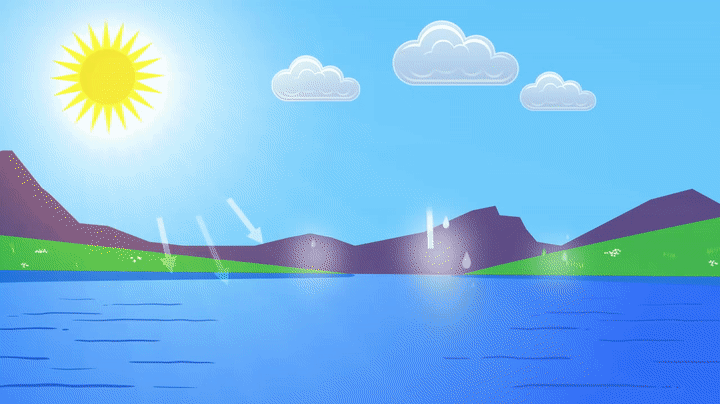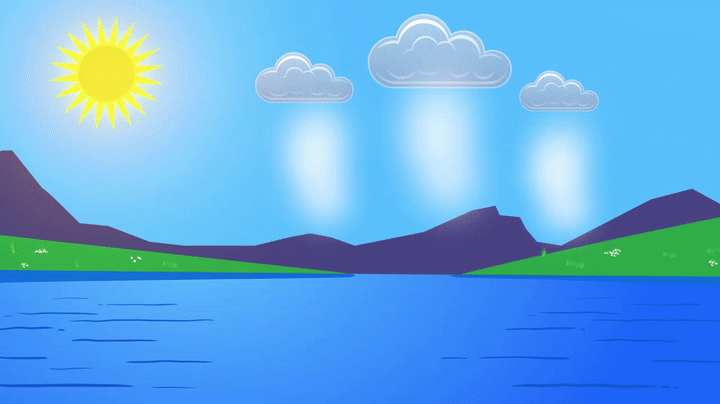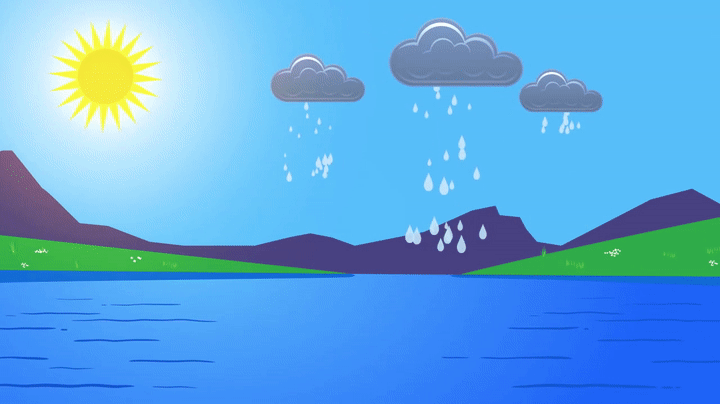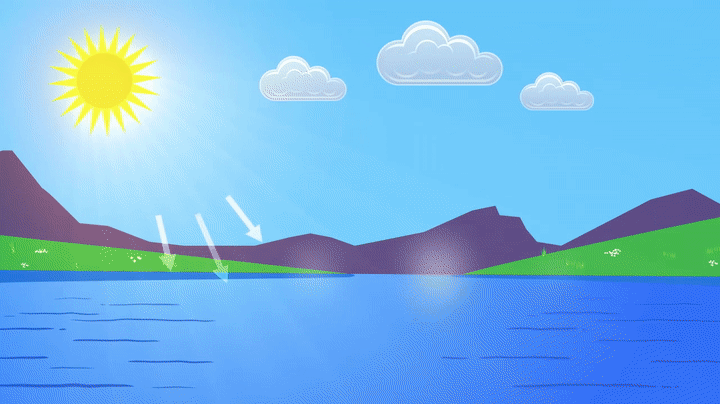
The water cycle describes how water moves around the Earth. It never stops and has neither a beginning nor an end. It resembles a large circle. We’ll start with water on land and work our way up. For example:
Water is found in the ocean or a lake. Because of the heat from the sun, some water on the ocean’s surface will evaporate. When it evaporates, it becomes vapor water and rises into the atmosphere. This vapor water combines with a large amount of other vapor water to form clouds.
Clouds move around the Earth with the weather, and once they are full of water, they release it as precipitation. It may rain, snow, sleet, or hail. When water hits the ground, it may fall back into the ocean, feed a flower, or form snow on the top of a mountain. This water will eventually evaporate, restarting the cycle.
Here are the three main ways that water on land evaporates:
Evaporation is the primary process by which water moves from the ground to the atmosphere as vapor. Evaporation is responsible for approximately 90% of the water vapor in the atmosphere. Evaporation occurs only on the water’s surface. It requires heat as an energy source.
Hot water evaporates faster than cold water. The sun provides a significant portion of the energy for evaporation in the water cycle, primarily causing evaporation from the ocean’s surface.
Sublimation is the process by which water moves directly from ice or snow to vapor without ever melting. Sublimation is most likely to occur when ice or snow is extremely cold but windy and the sun is shining.
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water onto their leaves, which then evaporates into vapor. Plants expel a lot of water as they grow. It is estimated that transpiration accounts for 10% of the water vapor in the atmosphere.
Water vapor in the atmosphere
Clouds are examples of water in the atmosphere. Even in clear skies, there is some water, but clouds are where water has begun to condense. Condensation is the transformation of water vapor into liquid water.
Condensation is a significant step in the water cycle. The atmosphere aids in the movement of water around the globe. It transports evaporated ocean water over land, where clouds and storms form, to water plants with rain.
Precipitation
Precipitation occurs when water falls from the atmosphere to the ground. When enough water accumulates in a cloud, droplets of water form and fall to the earth. This could be rain, snow, sleet, or even hail depending on the temperature and weather.
Storage of water
A large portion of the Earth’s water does not participate in the water cycle very frequently. Much of it has been saved. Water is stored in a variety of locations on Earth. The ocean is the world’s largest water storage facility.
The ocean holds approximately 96 percent of the Earth’s water. Because we cannot drink the salty ocean water, freshwater is stored in lakes, glaciers, snow caps, rivers, and beneath the ground in groundwater storage.