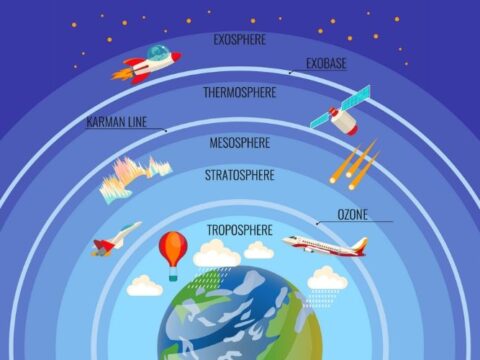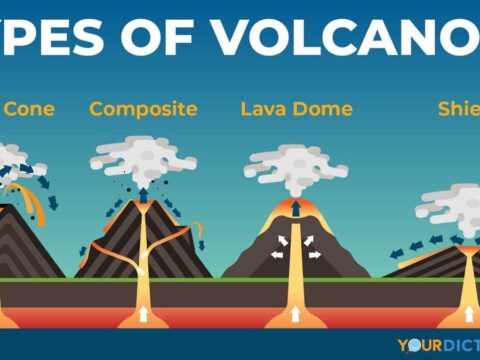
A network of interconnected food chains in an ecosystem is referred to as a food web. In the initial stages of a food web, there are typically many little animals present. In higher levels of a food web, there are fewer species that are larger in size.

There are several food webs, and some of them provide decomposers with a significant role. Decomposers are a diverse group of organisms that include worms, bacteria, and fungi. They consume dead plants and animals, which ultimately leads to their decomposition.
Decomposers are also responsible for the breakdown of animal manure. They disassemble everything into more manageable chemical components that we call nutrition.
The nutrients are then recycled back into the soil, where plants can use them along with water to produce new food. In a never-ending cycle, nutrients work their way through food webs.