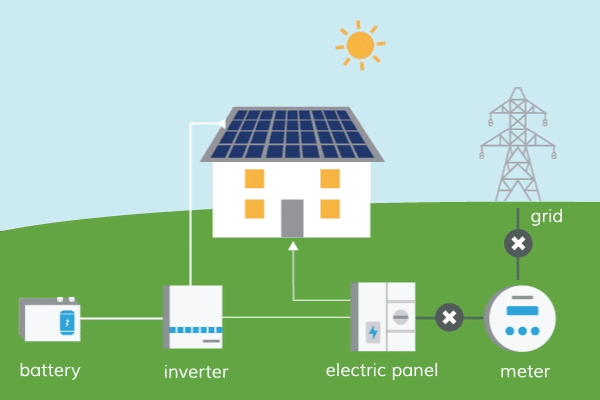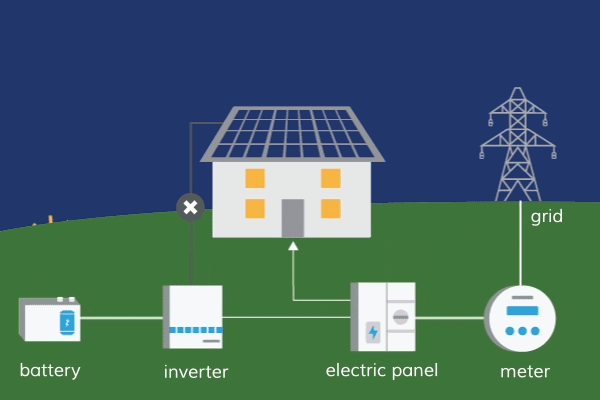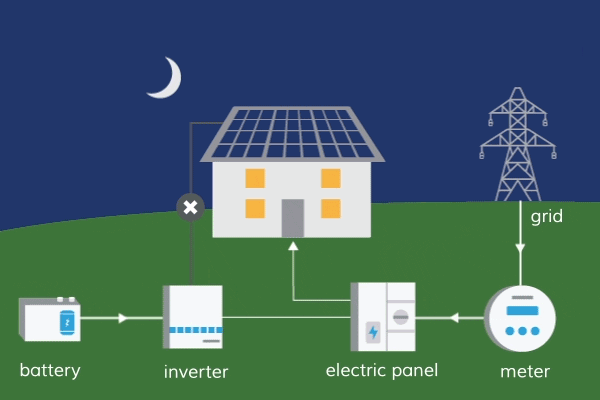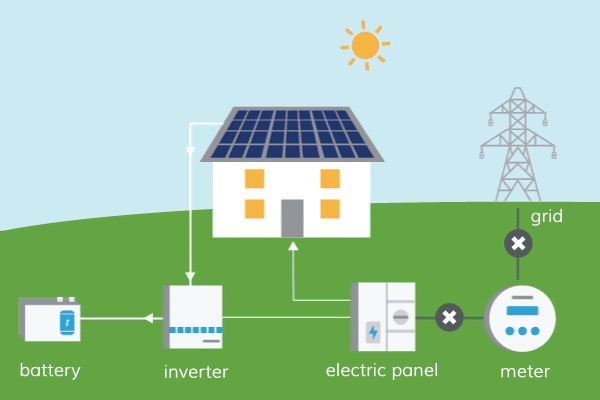
Nurturing a Sustainable Future
Conserving energy is an imperative that resonates across scientific, environmental, and societal landscapes. This exploration delves into the multifaceted aspects of energy conservation, examining its significance, the principles that underlie it, and the diverse strategies employed to foster a sustainable and responsible approach to energy usage.
The Imperative of Energy Conservation:
Energy, a finite and invaluable resource, serves as the lifeblood of modern society. The imperative to conserve energy arises from the need to address environmental concerns, enhance energy security, and promote sustainable development. As the global population burgeons and energy demands escalate, the judicious use and preservation of energy become paramount.
Principles of Conservation of Energy:
The foundation of energy conservation lies in the principles of the conservation of energy, which posits that the total energy in a closed system remains constant. While energy can change forms, it is neither created nor destroyed. This principle, articulated in the laws of thermodynamics, underscores the interconnectedness of energy forms and the significance of a balanced energy ecosystem.
Energy Efficiency:
Efficient Technologies: Enhancing energy efficiency involves adopting technologies that minimize energy waste. From energy-efficient appliances and lighting to advanced heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, technological innovations play a pivotal role in optimizing energy consumption across diverse sectors.
Industrial Practices: Industries can significantly contribute to energy conservation through streamlined processes, energy-efficient machinery, and waste heat recovery systems. Implementing energy management systems and conducting energy audits are effective tools to identify and rectify inefficiencies.
Renewable Energy Sources:
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is a cornerstone of sustainable energy practices. Solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass offer clean and replenishable alternatives to fossil fuels. Harnessing these sources reduces dependence on finite resources, mitigates environmental impacts, and contributes to a low-carbon future.
Smart Grids and Advanced Infrastructure:
Smart Grids: Smart grids integrate advanced communication and control technologies into traditional power grids. They enable real-time monitoring, efficient energy distribution, and demand-side management. Smart grids enhance the reliability and resilience of energy systems while optimizing energy usage.
Energy Storage: Developing efficient energy storage systems is crucial for managing intermittent renewable sources and balancing supply and demand. Advances in battery technologies, pumped hydro storage, and other storage solutions contribute to grid stability and flexibility.
Building Design and Urban Planning:
Energy-Efficient Buildings: Sustainable architecture emphasizes energy-efficient building design, incorporating features such as proper insulation, energy-efficient windows, and passive solar design. Green building practices aim to minimize environmental impact and optimize energy performance.
Urban Efficiency: Smart urban planning considers energy-efficient transportation systems, compact and sustainable city layouts, and the integration of green spaces. Implementing energy-efficient infrastructure in urban areas fosters sustainable communities and reduces the ecological footprint.
Transportation Efficiency:
Fuel Efficiency: Advancements in fuel-efficient technologies, such as hybrid and electric vehicles, contribute to reducing the energy intensity of transportation. Improving public transportation, promoting walking and cycling, and implementing intelligent traffic management systems further enhance transportation efficiency.
Sustainable Fuels: Transitioning to sustainable fuels, including biofuels and hydrogen, reduces the environmental impact of transportation. Research and development in alternative fuels play a pivotal role in achieving a more sustainable and energy-efficient transportation sector.
Behavioral Changes and Awareness:
Education and Awareness: Fostering awareness about the importance of energy conservation and sustainability is essential. Educational initiatives, public campaigns, and outreach programs can empower individuals and communities to adopt energy-efficient practices in their daily lives.
Behavioral Changes: Encouraging energy-conscious behaviors, such as turning off lights and appliances when not in use, adjusting thermostats responsibly, and minimizing water heating, cultivates a culture of conservation at the individual and community levels.
Government Policies and Incentives:
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping the energy landscape. Implementing regulations, incentives, and subsidies that encourage energy efficiency, renewable energy adoption, and sustainable practices incentivises businesses and individuals to prioritize conservation efforts.
The Economic and Environmental Impact:
Cost Savings: Energy conservation not only mitigates environmental impacts but also yields economic benefits. Businesses and individuals can experience significant cost savings through reduced energy bills, increased operational efficiency, and the long-term sustainability of resources.
Environmental Stewardship: By minimizing energy consumption and transitioning to cleaner sources, energy conservation contributes to environmental stewardship. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating air and water pollution, and preserving ecosystems are intrinsic to sustainable energy practices.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Technological Advancements: Continued research and development in energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy solutions, and energy storage systems are imperative to overcoming existing challenges and pushing the boundaries of sustainable practices.
Global Collaboration: Addressing energy conservation on a global scale necessitates collaboration between nations, industries, and communities. Sharing knowledge, technology transfer, and joint initiatives can accelerate progress toward a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
The journey toward energy conservation is a dynamic and collective endeavor. From the principles of the conservation of energy to the innovative technologies and strategies shaping our energy landscape, the pursuit of sustainability resonates across disciplines and sectors.
Embracing energy conservation not only safeguards our planet for future generations but also cultivates a resilient and harmonious coexistence with the environment.
As we navigate the challenges and opportunities on this path, the principles of energy conservation stand as guiding beacons, illuminating a future where responsible energy practices propel us toward a sustainable and thriving world.