
The Austrian monk Gregor Mendel was the first person to observe patterns of heredity in pea plants. In the 1860s, he conducted research and experiments on pea plants.
Mendel’s research focused, in part, on the characteristics that determine the height of individual pea plants.
Mendel came to the conclusion that the characteristics must be inherited characteristics that were passed down from the parent plants. Genes came to be the term used for these factors much later.
Genes are the fundamental hereditary units that can be found in cells.
The genes in an organism are responsible for determining its outward appearance.
For instance, a person’s height, eye color, hair color, and all of the other physical characteristics they have are all determined by the genetic information that is contained in their cells.
The genes in a plant are responsible for determining its adult height, the size of its leaves, and the type of fruit it will produce.
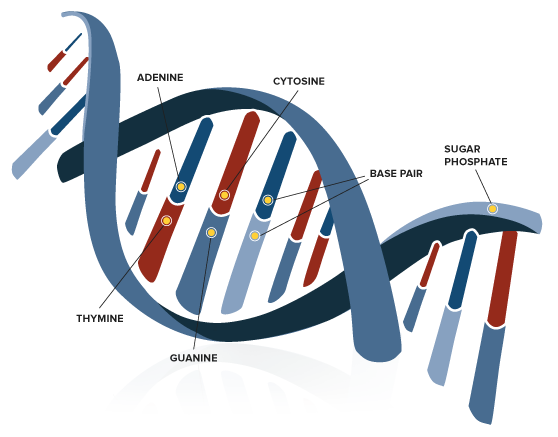
DNA is a term that refers to both the individual segments of nucleic acid that make up genes and the genes themselves. They do this by forming long chains that resemble threads and are called chromosomes.
The DNA contains a string of chemical instructions that specify how a cell is supposed to carry out its functions.
Chromosomes are always found in pairs inside every cell in the human body.
There are many genes on each chromosome, and each gene is positioned at a specific location on its respective chromosome. Genes are always found in pairs.
During sexual reproduction, the genes of the parents and the offspring are combined and the offspring receive one-half of their genes from each parent. This results in new combinations of genes, which allows each individual to be distinct while still retaining the genes that were passed down from their parents.
0 Comments






